

Pulse-shaped signal is equal to twice the symbol rate, then the bandwidth expansion factor If a raisedĬosine (RC) filter with a factor more than 1 is used, for which the bandwidth of the Pulse-shaped signal is equal to the symbol rate, then the bandwidth expansion factor is 1,Īnd at least one sample per symbol is required at the input to the channel. For example, if sinc pulse shaping is used, for which the bandwidth of the Kth path (in Hz), and θ L O S, k is the initial phase of the line-of-sight component of theĪt the input to the band-limited multipath channel model, the transmitted symbols mustīe oversampled by a factor at least equal to the bandwidth expansion factor introduced by Where K r, k is the Rician K-factor of the kth path, f d, L O S, k is the Doppler shift of the line-of-sight component of the The multipath fading channel is therefore modeled as a linear finite impulse-response This implementation assumes that the delay power profile and the Doppler spectrum of theĬhannel are separable. The Rayleigh and Rician multipath fading channel simulators in Communications Toolbox use the band-limited discrete multipath channel model of section 9.1.3.5.2 in Methodology for Simulating Multipath Fading Channels The Adaptive Equalization with Filtering and Fading Channel example illustrates why compensating for a fadingĬhannel is necessary. Modulation, see the M-DPSK Modulator Baseband block referenceĪn equalizer with multiple taps helps compensate for a frequency-selective fading For information about implementing differential Scattering effects, in addition to Doppler shifts that arise from relative motion betweenĭifferential modulation or a one-tap equalizer helps compensate for aįrequency-flat fading channel. Real-world phenomena in mobile communications.
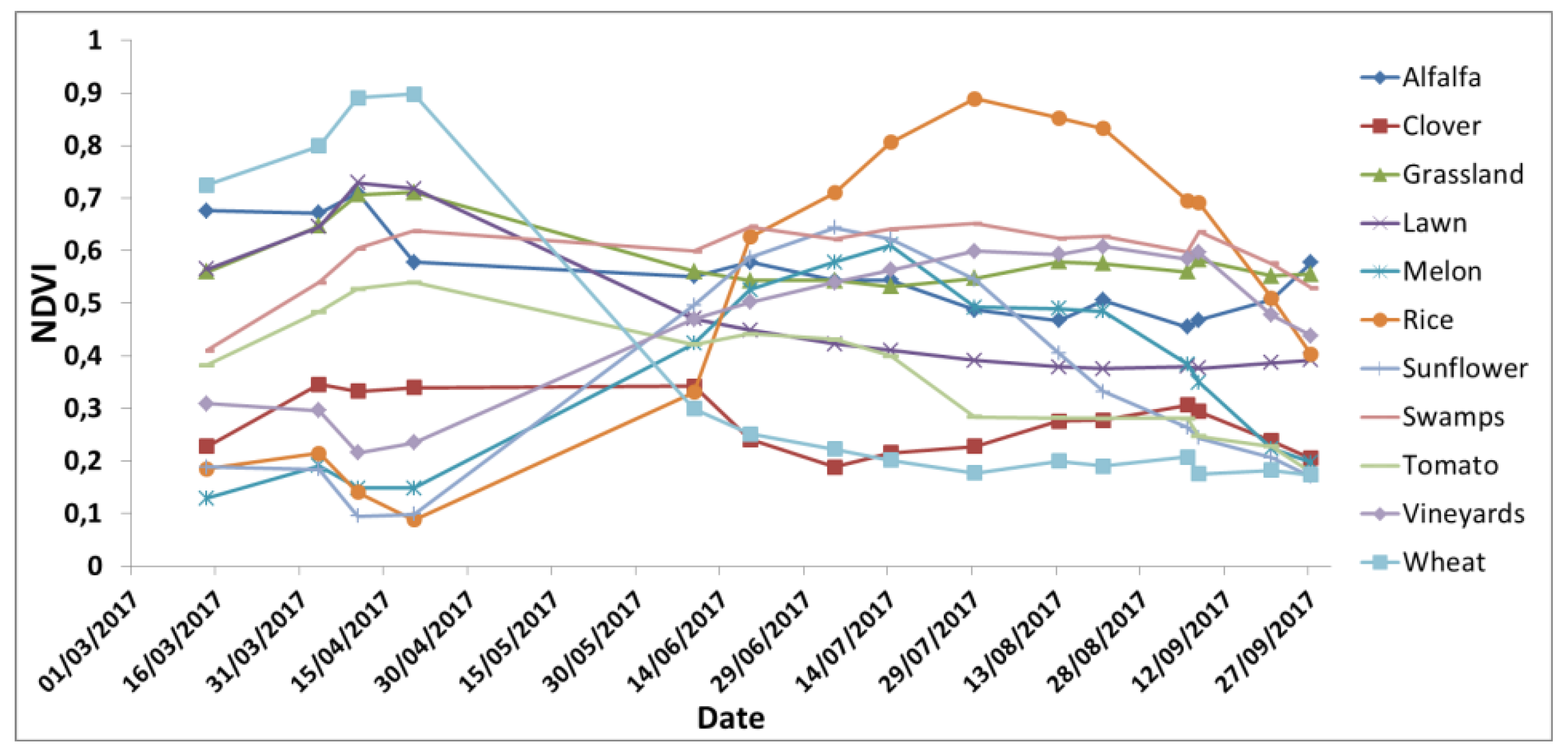
The Channels block library includes MIMO and SISO fading blocks that can simulate Some additional information about typical values for delays and gains is in Choosing Realistic Channel Property The fading does not evolve with time and the Doppler spectrum specified has no effect If the maximum Doppler shift is set to 0 or omitted during the construction of aĬhannel object, then the object models the channel as static. Gaussian, bi-Gaussian, rounded, and bell. Or different for all paths) include: flat, restricted Jakes, asymmetrical Jakes, Other types of Doppler spectra allowed (identical N > 1 is experienced as a frequency-selective fadingĬhannel by a signal of sufficiently wide bandwidth.Ī Rayleigh or Rician model for each path.ĭefault channel path modeling using a Jakes Doppler spectrum, with a maximumĭoppler shift that can be specified. A channel for which N = 1 is called aįrequency-flat fading channel. Each path has its own delay andĪverage power gain. The path gains are configured based on settings chosen in the fading channel object or The channel filter applies path gains to the input signal, Signal in. Whose direction exactly opposes the trajectory of the mobile. Maximum Doppler shift corresponds to the local scattering components Of Doppler shifts, known as the Doppler spectrum. Scattering typically comes from many angles around the mobile. The relative motion between the transmitter and receiver causes Doppler shifts. Rayleigh distribution for a non line-of-sight path and a Rician distribution for a Typically, the fading process is characterized by a Due to this phenomenon, each major pathīehaves as a discrete fading path. These irresolvable components combine at the receiver and cause a phenomenon Such local scattering typically results from reflections off objects near In addition, the radio signal undergoes scattering on a local scale forĮach major path. The major paths result in the arrival of delayed versions of the signal at the receiver.
Configure Channel Objects Based on Simulation Needs.Choose Realistic Channel Property Values.Create Rayleigh Channel Using Independent Doppler Spectrum.Create Rician Channel with Gaussian Doppler Spectrum.Create Rayleigh Channel with Flat Doppler Spectrum.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
